Network for Certification and Conservation of Forests (NCCF) Frequently Asked Questions on Forest Certification
Forests play a critical role in amelioration of the global environment, alleviating effects of climate change and natural disasters, conserve biodiversity, and are an integral part of soil water and carbon cycles. Sustainable forest management ensures improvement and continuance of these ecosystem services for present generation as well as for posterity.
Forest Management (FM) certification is a voluntary, non-regulatory and independent third party based tool to ensure sustainable management of forests in terms of being environmentally appropriate, socially beneficial and economically viable. It also ensures monitoring and helps in tracing, labelling and marketing of related forest products. It helps in verifying and bringing in missing but desirable components in management systems and practices and brings in enhanced creditability with international recognition and improves market accessibility of forest products.
Our country has multiple forests types and a diversity of scientific and traditional forest management practices. A country specific certification system ensures required flexibility and adaptability in addressing sustainable management needs of such a diverse forests.
A certification system outlines the rules, procedures and operational elements for carrying out certification. It establishes specific requirements for a product, process, system or body, and uses a third-party to ensure that the fulfillment of specified requirements has been demonstrated.
A credible certification system relies upon three separate functions as below, performed by independent organisations:
i. Standard setting is the process of defining certification requirements in collaboration with stakeholders and is coordinated by a standardizing body. (For India: NCCF)
ii. Certification is the process of checking whether an organization fulfills the certification requirements and is carried out by a Certification Body.
iii. Accreditation is the process of assessing the competence of the Certification Body and is carried out by an Accreditation Body. [For India: National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies (NABCB)
A credible certification system relies upon three separate functions as below, performed by independent organisations:
i. Standard setting is the process of defining certification requirements in collaboration with stakeholders and is coordinated by a standardizing body. (For India: NCCF)
ii. Certification is the process of checking whether an organization fulfills the certification requirements and is carried out by a Certification Body.
iii. Accreditation is the process of assessing the competence of the Certification Body and is carried out by an Accreditation Body. [For India: National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies (NABCB)
Standard development takes place using an open, transparent, consultative and consensus-based process that included a broad range of stakeholders. It is based on a standard setting document developed by the Standardizing Body following the international Benchmark Standards. The steps involved are:
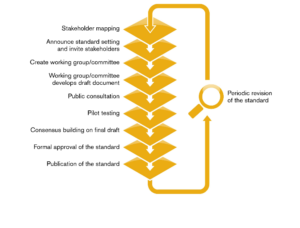

Certification Systems are developed based on certain procedures, benchmarks and guidelines defined by Standard setting organisations, and which follow international best practices to ensure utmost credibility
Accreditation Body is an independent functioning arm of the certification system. An Accreditation Body (AB) will periodically assess the competence of the certification bodies.
When developing a national scheme and certification system, a national Accreditation Body (AB) is preferred, which should mandatorily be a member of the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) or of one of the IAF regional accreditation groups.
When developing a national scheme and certification system, a national Accreditation Body (AB) is preferred, which should mandatorily be a member of the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) or of one of the IAF regional accreditation groups.
It is National Board for Accreditation of Certification Bodies (NABCB), a constituent Board of the Quality Council of India, which is also a member of the international body, International Accreditation Forum (IAF), and has signed the mutual recognition arrangements with the IAF.
Network for Certification and Conservation of Forests (NCCF), a not for profit organisation of India, is actively engaged in diverse conservation activities including, development of globally benchmarked and India specific sustainability certification standards for various constituents of our natural resource base, viz, Forest Management (FM), Trees outside Forests (ToF), Non-Wood Forest Produce (NWFP), Protected Areas and Wetlands (PAW), Quality Planting Material (QPM), Ecotourism and Biomass & Biofuels, etc.
The Indian scheme of forest management (FM) certification developed by NCCF, which is internationally benchmarked and country specific, has been endorsed by PEFC (Programme for Endorsement of Forest Certification), giving it an international recognition. The scheme was launched in January 2018 and got PEFC endorsement in February 2019 and has been operational since then. NCCF is the only member [National Governing Body (NGB)] of PEFC Council from India.
NCCF entered into a Mutually Recognition Arrangement (MRA) with NABCB for offering accreditation to competent certification bodies. NCCF FM Accreditation from NABCB demonstrates competence level of the Certification Bodies (CBs) to perform FM certification audits as per internationally recognized ISO 17065 Standard and NCCF Standards. CBs are accredited based on the organizational and technical competence of an organization to conduct certification activities like auditing and report writing. Also as part of accreditation requirement, NCCF conducted a three days NCCF FM Auditor Training for experienced forestry professionals in December 2019. The Indian scheme of forest management (FM) certification developed by NCCF, which is internationally benchmarked and country specific, has been endorsed by PEFC (Programme for Endorsement of Forest Certification), giving it an international recognition. The scheme was launched in January 2018 and got PEFC endorsement in February 2019 and has been operational since then. NCCF is the only member [National Governing Body (NGB)] of PEFC Council from India.
NCCF entered into a Mutually Recognition Arrangement (MRA) with NABCB for offering accreditation to competent certification bodies. NCCF FM Accreditation from NABCB demonstrates competence level of the Certification Bodies (CBs) to perform FM certification audits as per internationally recognized ISO 17065 Standard and NCCF Standards. CBs are accredited based on the organizational and technical competence of an organization to conduct certification activities like auditing and report writing. Also as part of accreditation requirement, NCCF conducted a three days NCCF FM Auditor Training for experienced forestry professionals in December 2019.
The Indian scheme of forest management (FM) certification developed by NCCF, which is internationally benchmarked and country specific, has been endorsed by PEFC (Programme for Endorsement of Forest Certification), giving it an international recognition. The scheme was launched in January 2018 and got PEFC endorsement in February 2019 and has been operational since then. NCCF is the only member [National Governing Body (NGB)] of PEFC Council from India.
NCCF entered into a Mutually Recognition Arrangement (MRA) with NABCB for offering accreditation to competent certification bodies. NCCF FM Accreditation from NABCB demonstrates competence level of the Certification Bodies (CBs) to perform FM certification audits as per internationally recognized ISO 17065 Standard and NCCF Standards. CBs are accredited based on the organizational and technical competence of an organization to conduct certification activities like auditing and report writing. Also as part of accreditation requirement, NCCF conducted a three days NCCF FM Auditor Training for experienced forestry professionals in December 2019. The Indian scheme of forest management (FM) certification developed by NCCF, which is internationally benchmarked and country specific, has been endorsed by PEFC (Programme for Endorsement of Forest Certification), giving it an international recognition. The scheme was launched in January 2018 and got PEFC endorsement in February 2019 and has been operational since then. NCCF is the only member [National Governing Body (NGB)] of PEFC Council from India.
NCCF entered into a Mutually Recognition Arrangement (MRA) with NABCB for offering accreditation to competent certification bodies. NCCF FM Accreditation from NABCB demonstrates competence level of the Certification Bodies (CBs) to perform FM certification audits as per internationally recognized ISO 17065 Standard and NCCF Standards. CBs are accredited based on the organizational and technical competence of an organization to conduct certification activities like auditing and report writing. Also as part of accreditation requirement, NCCF conducted a three days NCCF FM Auditor Training for experienced forestry professionals in December 2019.
Certification audit is carried out by the Certification Bodies (conformity assessment bodies) in short CBs, that are required to be accredited under an international system of accreditation, which in India is operated by the National Board for Accreditation of Certification Bodies (NABCB). NABCB provides accreditation (authorization) to various certification and inspection agencies in accordance with ISO standards, national guidelines and international requirements.
Chain of Custody (CoC) certification provides independently verified assurance that certified material contained in a product originates from sustainably managed forests. It traces the path of products from forests to markets through processing units and supply chain and ensures through tracing and labelling system that certified material is kept separate and is not mixed with uncertified material throughout the chain.
It also helps minimize the risk that forest products is from illegal harvesting and sourcing, and enables and it companies to demonstrate alignment with regulatory requirements (e.g. European Union Timber Regulation (EUTR). It also helps minimize the risk that forest products is from illegal harvesting and sourcing, and enables and it companies to demonstrate alignment with regulatory requirements (e.g. European Union Timber Regulation (EUTR).
It also helps minimize the risk that forest products is from illegal harvesting and sourcing, and enables and it companies to demonstrate alignment with regulatory requirements (e.g. European Union Timber Regulation (EUTR). It also helps minimize the risk that forest products is from illegal harvesting and sourcing, and enables and it companies to demonstrate alignment with regulatory requirements (e.g. European Union Timber Regulation (EUTR).
NCCF-FM standard incorporates all internationally benchmarked sustainable management principles, criteria and indicators including the components of National Working Plan Code 2014. Thus, if a forest division is certified as per NCCF-FM standard, it improves its management and gives an independent, third party assurance that management systems are environmentally appropriate, socially beneficial and economically viable. It also ensures that related forest products will have a credible and internationally recognized label, to help access the global markets as well as gain preference from environmentally conscious domestic consumers.
i. Environmental Benefits:
Certification enables Forest Departments to manage forests while maintaining environmental safeguards including - use of permissible pesticides, safe collection and disposal of toxic wastes, controlling invasive species, minimising negative impact on soil and water resources, enhancing ecosystem services and identification and management of high conservation value forests.
ii. Economic Benefits:
Forest certification enables the forest managers and stakeholders to get premium price for their products and facilitates value addition and access to the new markets apart from brand recognition due to use of certification logo and international recognition of good management.
iii. Monitoring Benefits:
Certification being Independent third-party evaluation adds value and credibility to the findings of periodic monitoring, and thus enables the forest departments to keep check on desired outcomes from their management interventions.
iv. Management Benefits:
It will bring the forest management at par with internationally benchmarked practices. Additionally, it strengthens regular capacity building of staff and workers, which catalyzes efficiency in operations, emphasis on value addition, improved marketing with better markets, better product positioning and visibility.
v. Safeguards Social Attributes:
It contributes towards social and gender equity, enhancing livelihood opportunities for locals, health and safety for forest workers, respecting rights of tribal and local communities and active engagement with the stakeholders.
vi. Compliments Country’s International Commitments:
Forest certification contributes to promoting SFM, REDD+, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), commitments under the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and in meeting the objectives of various international commitments under the UNFCCC, UNCCD and UNCBD, etc.
Certification enables Forest Departments to manage forests while maintaining environmental safeguards including - use of permissible pesticides, safe collection and disposal of toxic wastes, controlling invasive species, minimising negative impact on soil and water resources, enhancing ecosystem services and identification and management of high conservation value forests.
ii. Economic Benefits:
Forest certification enables the forest managers and stakeholders to get premium price for their products and facilitates value addition and access to the new markets apart from brand recognition due to use of certification logo and international recognition of good management.
iii. Monitoring Benefits:
Certification being Independent third-party evaluation adds value and credibility to the findings of periodic monitoring, and thus enables the forest departments to keep check on desired outcomes from their management interventions.
iv. Management Benefits:
It will bring the forest management at par with internationally benchmarked practices. Additionally, it strengthens regular capacity building of staff and workers, which catalyzes efficiency in operations, emphasis on value addition, improved marketing with better markets, better product positioning and visibility.
v. Safeguards Social Attributes:
It contributes towards social and gender equity, enhancing livelihood opportunities for locals, health and safety for forest workers, respecting rights of tribal and local communities and active engagement with the stakeholders.
vi. Compliments Country’s International Commitments:
Forest certification contributes to promoting SFM, REDD+, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), commitments under the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and in meeting the objectives of various international commitments under the UNFCCC, UNCCD and UNCBD, etc.
Many State Forest Departments have initiated action for certification of a few forest divisions. Recently, Uttar Pradesh Forest Corporation (UPFC) has taken up certification of 13 forest divisions with an area of around 4 lakh hectares using NCCF Forest Management Certification Scheme.
The clients (State Forest Department, State Forest Department Corporation, Corporates, Companies, domestic and international Buyers etc.) have to bear the certification cost. Cerification cost depends on area to be certified, type of forests, complexity of management systems etc. NCCF would be ready to help in working out cost estimation.
Forest certification and development of certification standards are eligible activities under Compensatory Afforestation Fund Rules, 2018 is one provision for financing certification expense. Besides states can use other financial provisions too.
Forest certification and development of certification standards are eligible activities under Compensatory Afforestation Fund Rules, 2018 is one provision for financing certification expense. Besides states can use other financial provisions too.
Notifications means that a Certification Body has been recognized by NCCF to perform audit against NCCF Certification Standards following certain rules and regulations as presented in the accreditation and certification requirements for CBs operating the NCCF FM Certification Scheme.Forest certification and development of certification standards are eligible activities under Compensatory Afforestation Fund Rules, 2018 is one provision for financing certification expense. Besides states can use other financial provisions too.
Once certified client becomes eligible to use NCCF/PEFC logo on-products and off-products, as an assurance that product has been sourced from a certified forests.
Globally the two most well-known forest certification systems are Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) and Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), both committed to the cause of SFM. Together, PEFC and FSC have certified around 525 million hectares of forests across the world.
PEFC, established in 1999, is an international non-profit, non-governmental organisation promoting SFM through third-party certification. It is an umbrella organization that works by endorsing nationally developed forest certification schemes, following the PEFC Benchmark Standards, under a mutual recognition system. PEFC is now a leading global alliance of 53 national members, with 46 endorsed national forest certification systems, accounting for around 325 million hectares of certified forests. The Indian Forest Certification Scheme developed by NCCF has been endorsed by the PEFC.
PEFC, established in 1999, is an international non-profit, non-governmental organisation promoting SFM through third-party certification. It is an umbrella organization that works by endorsing nationally developed forest certification schemes, following the PEFC Benchmark Standards, under a mutual recognition system. PEFC is now a leading global alliance of 53 national members, with 46 endorsed national forest certification systems, accounting for around 325 million hectares of certified forests. The Indian Forest Certification Scheme developed by NCCF has been endorsed by the PEFC.
PEFC Endorsement and Mutual Recognition helps national certification systems to gain international recognition for the national forest management standard and sustainable management practices in that country’s forests and provide the certified entities with market access through PEFC. The prime objective of PEFC Endorsement is to determine whether a national forest certification system meets PEFC Sustainability Benchmarks and conformance to PEFC requirements.